In this article, you will learn about the C++ queue and its methods with some useful example programs which would help you understand the concept better.
QUEUE IN C++ STL
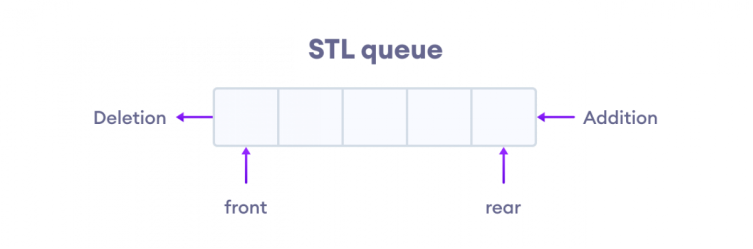
Queues are a type of container adaptors that operate in a first in first out (FIFO) type of arrangement. In a queue, the elements are inserted from the rear and removed from the front.
Creating a Queue
Before using the queue, we must include the <queue> header which has all the operations of the queue.
So now that we have included the <queue> header file we can create a queue using the following syntax.
Syntax:
queue<type> q;Here the type indicated the type of data that we want to store in the queue which is similar to the stack syntax.
// create a queue of integer data type
queue<int> integer_queue;
// create a queue of string data type
queue<string> string_queue;Queue Methods
Now let’s look at some queue Methods. The STL queue has several methods to perform different operations on a queue.
- push(i) – this method is used to insert the element I at the end of the queue.
- pop() – the pop() method is used to remove an element from the queue and the element is removed from the front of the queue.
- front() – Returns the first element in the queue
- back() – Returns the last element or the latest element in the queue.
- size() – Returns the size i.e., the number of elements in the queue.
- empty() – This empty() method is similar to the stack empty() method it checks whether the queue is empty or not and returns true if the queue is empty.
Adding Elements to a Queue
We will use the push() method to insert an element to the rare end of the queue.
For example,
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a queue of string
queue<string> animals;
// push elements into the queue
animals.push("Cat");
animals.push("Dog");
cout << "Queue: ";
// print elements of queue
// loop until queue is empty
while(!animals.empty()) {
// print the element
cout << animals.front() << ", ";
// pop element from the queue
animals.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Queue: Cat, Dog,In the above example, we have created a queue of strings called animals and added elements using the push() method.
animals.push("Cat");
animals.push("Dog");To print the queue we use the while loop along with the front() and pop() methods.
Removing Elements from a Queue
We use the pop() method which removes the element from the front of the queue.
For example,
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// function prototype for display_queue utility
void display_queue(queue<string> q);
int main() {
// create a queue of string
queue<string> animals;
// push element into the queue
animals.push("Cat");
animals.push("Dog");
animals.push("Fox");
cout << "Initial Queue: ";
display_queue(animals);
// remove element from queue
animals.pop();
cout << "Final Queue: ";
display_queue(animals);
return 0;
}
// utility function to display queue
void display_queue(queue<string> q) {
while(!q.empty()) {
cout << q.front() << ", ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
Output
Initial Queue: Cat, Dog, Fox,
Final Queue: Dog, Fox, Accessing the Elements from a Queue
We can access the elements of a queue by using either of the functions, front() or back()
front() – returns the element from the front of the queue
back() – returns the element from the back of the queue
For example,
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// create a queue of int
queue<int> nums;
// push element into the queue
nums.push(1);
nums.push(2);
nums.push(3);
// get the element at the front
int front = nums.front();
cout << "First element: " << front << endl;
// get the element at the back
int back = nums.back();
cout << "Last element: " << back << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
First element: 1
Last element: 3In the above example, 1 was inserted first so the front() method returns 1 and the last element that was inserted into the queue was 3 so the back() method returns 3.
That is all for this article. Let’s learn about the priority queue in the next one.
Happy Coding!


