INTRODUCTION
MAP CONTAINER in Cpp
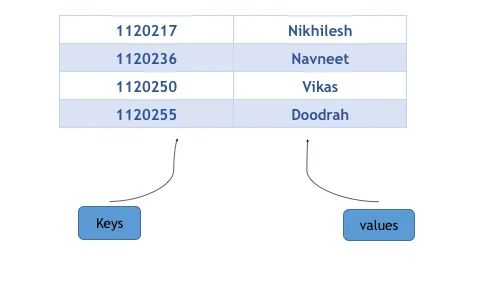
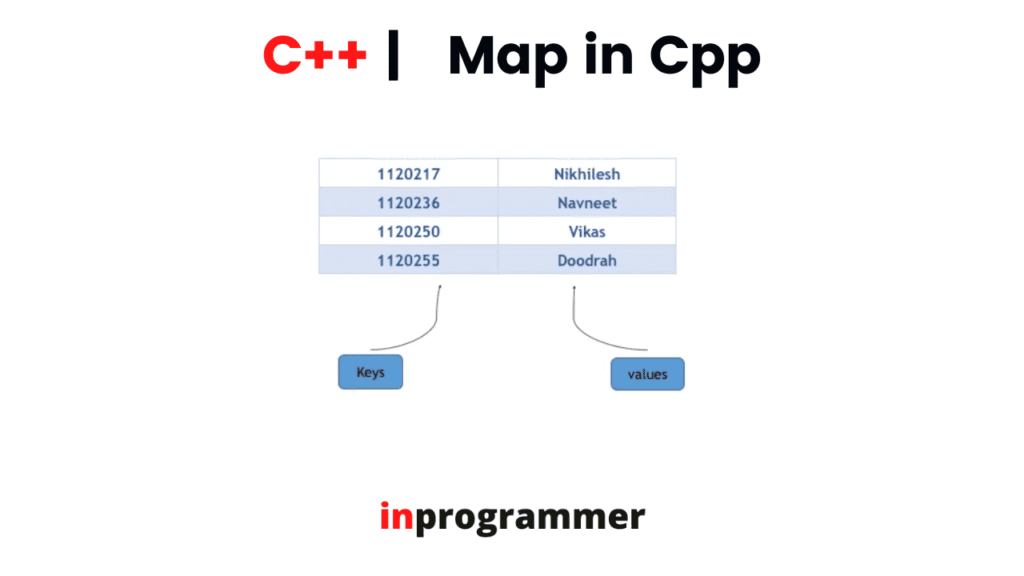
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about map containers from the standard template library of C++. The map is an associative container that stores items in a mapped form. Each item in the map is a combination of a key-vale and a mapped value. The key values in the maps are unique, that is no two mapped values cannot have the same key value. The key values in the maps are used for sorting and identifying the elements and the mapped values are used to store the content of the respective key. The key-vale and the mapped value in the map are associated using the keyword “pair”.
Here are some of the points noted about the map.
- Maps store the mapped values associated with unique key values stored in some specific sorting order based on the specific sorting criteria.
- The keys in maps are used for faster searching of the values associated with them.
- Only one value is associated with one key value.
- Maps used binary tree implementation. Maps can be used as an associative array.
let’s look at the syntax of the map container.
map< key_datatype , value_datatype > map_name;Where key_datatype and value_datatype represent the datatypes of the key and values respectively.
Let’s look at some of the basic methods that are implemented on the map container.
insert(): this method adds a new item to the map in a specific order
erase(): this method removes the particular item from the map.
begin(): this method returns an iterator to the first element in the map.
end(): this method returns an iterator to the last element in the map.
size(): this method is used to return the number of items stored in the map.
max_size(): this method returns the maximum number of elements that a map can hold.
empty(): this method returns a boolean value whether the particular map is empty or not.
clear(): this method is used to remove all the elements from the map and empty it.
These are some of the basic methods that are implemented on the map container.
Let’s look at a sample program implementing the map container.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<int, string> S;
S.insert(pair<int, string>(1, "Alice"));
S.insert(pair<int, string>(2, "John"));
S.insert(pair<int, string>(3, "carry"));
S.insert(pair<int, string>(4, "leo"));
S.insert(pair<int, string>(5, "james"));
S.insert(pair<int, string>(6, "stephen"));
cout << "Map size is: " << S.size() << endl;
cout << endl << "Default map Order is: " << endl;
for (map<int, string>::iterator it = S.begin(); it != S.end(); ++it) {
cout << (*it).first << ": " << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout<<"\nvalue associated with key_value 6 : \n"<<S[6];
}
The output of the program is.

In the above program, we have included the < map > header to create a map container. Following the syntax, we have created a map named S and inserted the key_value pairs using the insert function. Then an iterator itr is created and made to traverse over the map to get the respective key_value pairs. We have counted the number of items stored in the map by using the size() method. after using normal slicing, we have found the mapped value associated with a particular key. This is the implementation of the map container.
The map and the unordered_map are almost similar, then what is the one thing that differentiates the map from the unordered_map?
Let’s look at the differences between the map and the unordered_map.
| MAP | UNORDERED_MAP |
| The maps are implemented the using binary search tree | The unordered_maps are implemented using the hash tables. |
| The items in the map are stored in the increasing order of the key_value regardless of how they are inserted. | The items in the unordered_map are stored in the order in which they are inserted. |
| For searching an item: O( logN ) | For searching an item: O( 1 ) ->average time complexity O( n ) -> worst time complexity |
| For insertion and deletion : O( logN ) | For insertion and deletion : O( 1 ) -> average time complexity O( n ) -> worst time complexity |
CONCLUSION
That’s it from this tutorial. We have learned about the map container, its properties, basic methods that are implemented on maps, and differences between the maps and the unordered_maps. Hope you guys found it interesting. Happy Coding!